Session (7)
Step 6: Dissemination of Evidence

- Dissemination is the targeted distribution of information and intervention materials to a specific public health or clinical practice audience. The intent is to spread knowledge and the associated evidence-based interventions.
-
Dissemination occurs through a variety of channels, social contexts, and settings. Evidence dissemination has several very broad goals: (1) to increase the reach of evidence; (2) to increase people’s motivation to use and apply evidence; and (3) to increase people’s ability to use and apply evidence.
-
Dissemination is an important component of translation of evidence because if the translation is not disseminated, then no change in care will occur and innovations will not be adopted.
-
Dissemination is the communication of clinical, research, and theoretical findings for transitioning new knowledge to the point of care.
-
Dissemination occurs at multiple levels. Once the translation project is complete, the first area for dissemination is internal. Next, information should be disseminated at the institutional level. This can be accomplished through hospital or organizational professional committee meetings or journal clubs.
-
There are three main methods of (external) dissemination, also known as the three Ps: posters, presentations, and papers. In addition, external dissemination intended to influence policy may occur through the use of media or government advocacy.
-
Dissemination is most successful if multiple methods are used over time.
-
Once research has been completed, and the results of the evidence-based process have been collected, it is important for the knowledge obtained to be shared with other clinicians.
-
Other clinicians, facilities, and patients can benefit from one individual or team’s hard work, and additional research may be prompted. This dissemination of knowledge also serves to inspire other nurses to form their own clinical questions and develop their own research. It inspires confidence and a feeling of autonomy in the nursing practice.
-
The distribution of results is the final reward in the long EBP process. Preparing and presenting a poster is an effective and often preferred method of dissemination. Others may choose to submit findings for publication in a journal or discuss their findings locally in a case study presentation.
-
In the case scenario, the wound nurse creates a poster presentation, which is presented at Samford University’s annual conference. The poster is also displayed at the local school of nursing and on the medical-surgical unit where the study was completed.
-
Effective dissemination is characterized by positive engagement of the targeted audience, which enhances awareness, understanding and motivation to implement in the workplace. The choice of dissemination methods depends on the targeted audience. Healthcare audience is mostly interested on how specific evidence fit into a specific context and the implications of adopting the changes on various aspects, such as policy, quality of care, staffing and funding among other aspects.
-
The internal method that I would use to disseminate the evidence-based practice is the hospital board. Hospital board essentially comprises of the employees of the health organization, such as nurses, physicians and other professionals involved in patient care. While disseminating the EBP to the hospital board the most appropriate method to apply would be face to face. The approach facilitates interaction and instant feedback especially during questioning sessions.
-
The external method that I would apply is presentation in conferences of professional organizations, particularly American Nurses Association. The professional organization would provide an ideal platform to facilitate dissemination of the project to large audience of nurses. The method that I would use in the conference is face to face to facilitate consultation and discussion with other nursing professionals. The communication strategies applied would vary in the internal and external forums. For instance, the hospital board comprises of colleagues, which implies that the communication would be less formal and more interactive compared to presentation in American Nurses Association conference.
-
Presentation of my evidence-based results to the two groups is important to facilitate sharing of the knowledge and information in the nursing fraternity. This would enhance decision-making capability among the group members involved in nursing practice and promote patient outcomes. Moreover, reporting the findings to the groups would facilitate constructive criticism of the results, thereby providing an opportunity to improve them before implementation.
-
Dissemination strategies aim to spread knowledge and the associated evidence-based interventions on a wide scale within or across geographic locations, practice settings, or social or other networks of end-users such as patients and health care providers. In examining influences that help spread innovations along the continuum between passive diffusion of information and active dissemination.
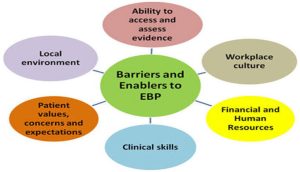
Barriers to Evidence-Based Practice
- First, undergraduate nursing students report positive feelings about using EBP and research but are not well prepared to apply EBP. It is imperative that undergraduate nurses are comfortable with EBP because these are the nurses that spend the most time with patients providing direct patient care.
-
Nurses also report a lack of resources required to implement EBP. EBP must be prioritized at the institutional and governmental levels for nurses to have the resources and training needed.
-
Some nurses report cultural disadvantages and negative attitudes about EBP, which leads to a lack of confidence in practicing EBP.
-
Another barrier to EBP is the time delay seen between the collection of research results and the application of those results. Nurses report that improved education, increased motivation, and acceptance of EBP by their employer increase the use of EBP.